Hey data folks — do any of these “quick requests” sound familiar?
- You store an enum as an array in your warehouse in camelcase, but in Salesforce, the picklist values are title case.
- You have event tables for each type of product event, but the Marketing team wants a rollup count of “product events in last 90 days.”
- The Growth team wants to do a quick AI summarization and data extraction on support tickets to update a HubSpot field with that information.
Each of these requests can be done quickly, but creating 1 new column always leads to 10 more asks. Supporting business requests can feel like death by a thousand cuts.
What if business teams could self-service their data transformation needs?
The ideal state is a place where both data and business teams can collaborate to create transformations, with or without code, and with the same set of trusted data. That's what we set out to create with Computed Columns, a feature of our Datasets product.
 |
Data Transformation, a Cross-Functional Team Sport
With our recent launch of Datasets, we announced our commitment to building the most powerful data transformation and collaboration tools. Today, we’re making good on that promise with Computed Columns: a no-code tool that makes last mile transformations easy, while still being fully governed, tracked, and observed by your data stack.
Computed Columns give business teams the tools they need to explore and analyze the data available to them and calculate the data points they need to answer key questions. We have the following types of Computed Columns in General Availability, with more coming soon:
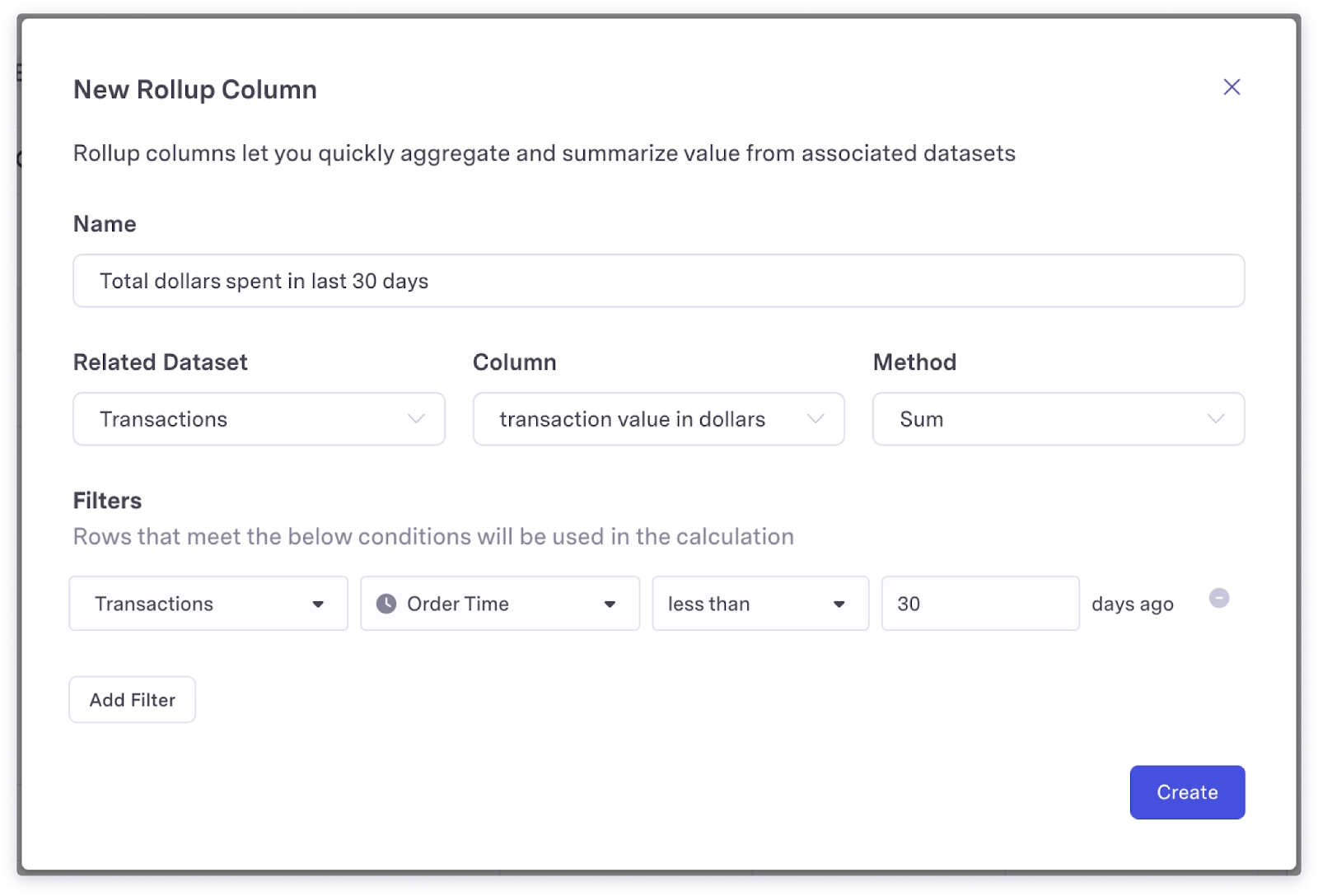
Rollup
Rollup Columns allow you to count the number of related records to understand volume within a certain group. For example:
- Total dollars spent on transactions last 30 days
- Count of transactions performed last 30 days
- Count of payment failures last 90 days
- Number of current active admin users
- First time purchased at
- Last login at
 |
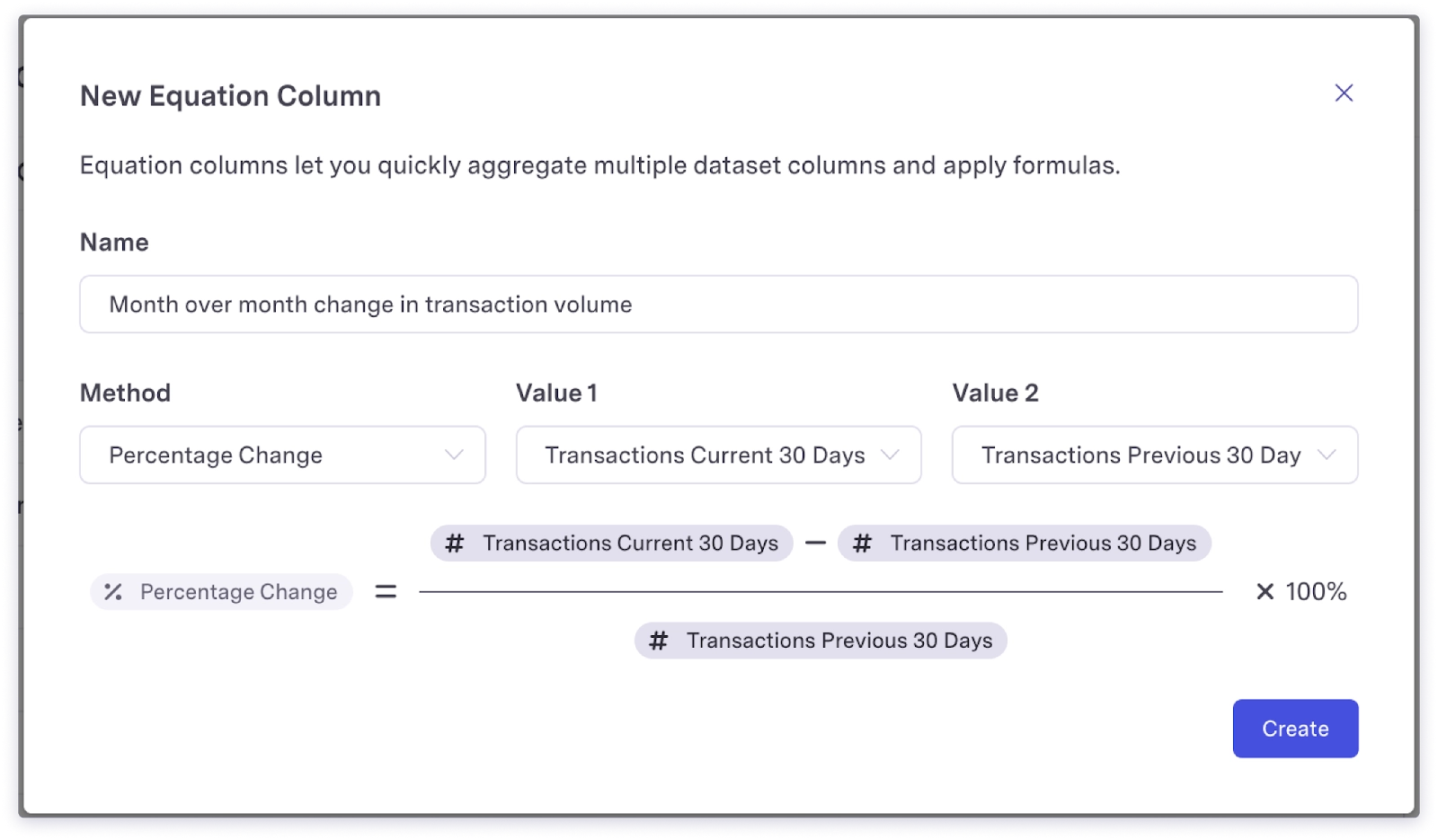
Equation
Equation Columns allow you to calculate data from recent events or related objects easily. For example:
- Month over month change in transaction volume
- Average cart amount in last 12 months
- Sum of all subscription amounts (Lifetime Value)
- Weekly growth rates of feature usage
- Difference month over month of documents shared
 |
Coming soon: More types of Computed Columns
Lookup
Lookup Columns help you quickly and simply denormalize data — it’s just a look-up away. For example:
- Associated team_name on the contact object through the team object
- Sales Segment from the Company object to Contact object
- Company_employee_count from the 3rd party enrichment dataset to the Company object
Text Transform
Sometimes, you want something more powerful than rollup or lookup but don’t want to go full code. This is where Liquid templating comes in handy. For example:
- When you want to transform your array of 5 values into 3 values that match to the corresponding picklists in Salesforce
- When you want to quickly transform camelCase names to Title Case to make them more readable
GPT Column
GPT Columns offer endless possibilities if you know how to prompt an LLM. For example:
- Creating company tags from a company description, such as identifying company industry or tagging companies as B2C or B2B
- Summarizing support tickets to extract sentiment
- Extracting technologies from job descriptions from 3rd party providers
- Clean company names, such as turning - Adeño LLc into Adeno
GPT columns are the most advanced Census Computed columns, with advanced options like prompt preview, enforced JSON answers, system and user prompts, and fallback methods. These ensure that high-quality data always returns.
What’s next: More powerful columns and more collaboration
Code Columns
When out-of-the-box Computed Columns are not enough, we let you run Python code. For example, you can look up the properties of a customer’s last purchase and convert the amount from a string such as USD 42.00, to an integer on your customer object to conform to the format required in Braze. More documentation coming soon.
Data Request Columns
There will still be times when data consumers don’t know how to do a transform. Business teams who need additional data or more help can use a Data Request Column, which creates a task for data teams to provide the right data. This automatically syncs to existing data team workflows, like a Git repo or task tracker. Once done, requesters will be notified and can use the new data immediately in syncs or segments.
With more columns and transformation, we will give you the option to materialize the values back to your warehouse and also make them accessible via our Dataset API.
Get started today
Computed Columns are a powerful tool within Census Datasets that allow data and business teams to explore, transform, and activate trusted data together. Over the next 6 months we’re building more features that unlock superpowers for data teams and make collaboration with a trusted data layer even easier.
Computed Columns and Datasets are available now. Get started with a free 14-day trial or reach out for a personalized onboarding.